The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare promises to transform patient outcomes and increase operational efficiency. However, this technological revolution brings with it significant ethical concerns, particularly in the areas of patient privacy, data security, and equitable care. This article explores the ethical considerations of leveraging AI in healthcare, focusing on balancing efficiency with the preservation of patient privacy.
The Promise of AI in Healthcare
AI offers numerous advantages, such as enhancing diagnostic precision, optimizing treatment plans, and predicting patient deterioration for timely intervention. AI-driven tools have demonstrated superior accuracy in identifying conditions like lung cancer, often surpassing human clinicians in diagnostic precision (NCBI, 2023a). Additionally, AI can streamline administrative tasks, manage patient records, and reduce the burden on healthcare professionals, leading to improved operational efficiency (NCBI, 2023b). These capabilities position AI as a powerful tool for advancing healthcare delivery.
Ethical Challenges: Patient Privacy and Data Security
Despite the potential benefits, the transition to an AI-augmented healthcare system raises significant ethical concerns. Chief among these is the issue of patient privacy. AI systems rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively, which necessitates the collection, storage, and analysis of sensitive patient information. This process inherently risks breaches of privacy, as AI systems can sometimes operate as "black boxes," making it difficult to ensure data is handled responsibly (SuperBill Blog, 2023).
Protecting patient privacy in this context requires rigorous data protection measures, including robust encryption, anonymization, and strict access controls. Furthermore, compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. is essential to safeguarding patient data (HITRUST, 2023).
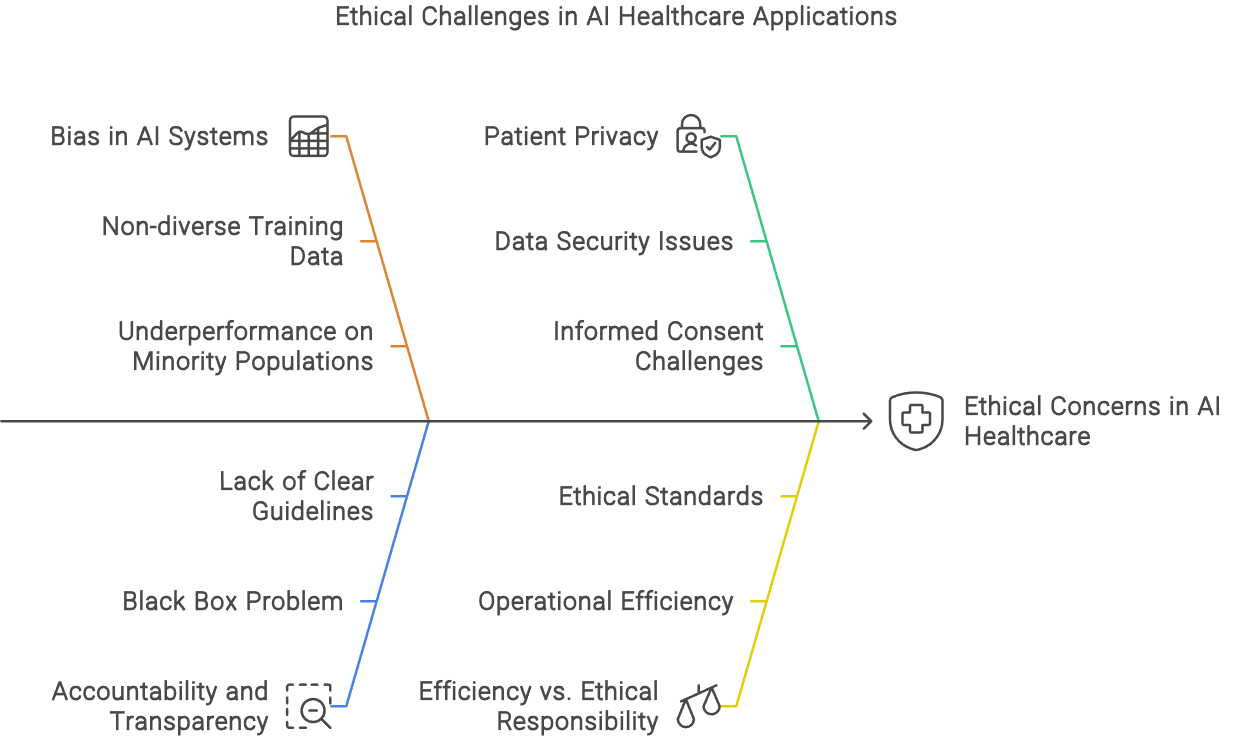
Addressing Bias and Ensuring Fairness
Another pressing ethical concern is the potential for bias in AI systems. AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on; if the training data is biased, the AI will likely perpetuate those biases. This issue is particularly problematic in healthcare, where biased algorithms could lead to disparities in care. For example, studies have shown that AI diagnostic tools may underperform on minority populations due to non-diverse training datasets (NCBI, 2023a).
To mitigate this risk, it is crucial to incorporate diverse and representative data during the development of AI systems. Techniques such as fairness-aware machine learning and ongoing algorithm auditing are essential for ensuring that AI models deliver equitable healthcare outcomes (NCBI, 2023b).
Ensuring Accountability and Transparency
Accountability and transparency are fundamental to the ethical use of AI in healthcare. AI systems must be transparent in their decision-making processes to foster trust among healthcare providers and patients. The opacity of AI, often referred to as the "black box" problem, can lead to a lack of understanding and trust in AI-driven decisions (SuperBill Blog, 2023).
Establishing clear guidelines for accountability is also crucial. There must be a clear delineation of responsibility for AI-driven decisions, ensuring that healthcare providers can audit and validate these decisions. Regulatory frameworks that mandate transparency standards and require AI systems to provide explainable outputs are vital in this regard (HITRUST, 2023).
Balancing Efficiency with Ethical Responsibility
The integration of AI in healthcare offers a pathway to significantly improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency. However, this must be balanced with ethical responsibility, particularly concerning patient privacy, bias, and accountability. By addressing these challenges, stakeholders can ensure that AI is used in a way that enhances healthcare while upholding the highest ethical standards.
Collaborative efforts between technologists, healthcare providers, and policymakers are essential to build a healthcare ecosystem that leverages AI's capabilities responsibly. This collaboration will help create AI systems that not only deliver on their promise of efficiency but do so in a way that is equitable, transparent, and trustworthy.
Conclusion
AI in healthcare holds the potential to revolutionize patient care and operational processes. However, to realize this potential fully, it is imperative to navigate the ethical challenges it presents. By prioritizing patient privacy, addressing bias, and ensuring transparency and accountability, the healthcare industry can harness AI's power while maintaining trust and equity in patient care. As we move forward, continuous dialogue and collaboration among all stakeholders will be crucial in shaping the ethical landscape of AI in healthcare.
References
- HITRUST. (2023, November 15). The Ethics of AI in Healthcare. Retrieved from https://hitrustalliance.net/blog/the-ethics-of-ai-in-healthcare/
- NCBI. (2023, August 10). Ethical Issues of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine and Healthcare. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8826344/
- NCBI. (2023, August 10). Unraveling the Ethical Enigma: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10492220/
- SuperBill Blog. (2023, November 21). AI in Healthcare Ethics — The SuperBill Blog. Retrieved from https://www.thesuperbill.com/blog/ai-in-healthcare-ethics-what-to-make-of-healthcare-automation/